Introduction
In concave mirror Qsolution's post you are going to learn:-
- About the Concave Mirror
- Important Terms of Concave Mirror
- Image Formation in the case of Concave Mirror
- Method to Draw Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror
- Magnification in the case of Concave Mirror
- Mirror Formula of Concave Mirror
- Uses of Concave Mirror
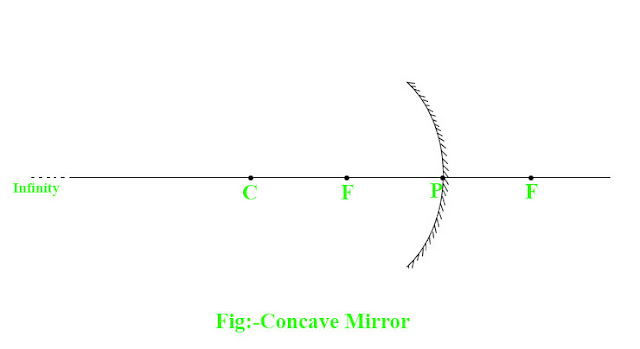
Concave Mirror
Concave mirror is a spherical curved mirror in which reflection takes place in the inner surface of the sphere of which the mirror is a part. Concave mirror has depressed inward at middle on the reflecting surface. It looks like you are looking into a cave. Outer surface of the concave mirror has painted as shown in figure below.
Concave mirror converges the incomming rays of light when they strike on the reflecting surface of the mirror. Hence, it is also known as the converging mirror. Image formed by concave mirror varies in size and position depending on the position of the object eith respect to the mirror. When an object has placed very close to the concave mirror within the focus, a magnified and virtual image of object has obtained behind the mirror. But if the distance between mirror and object increases, the size of image reduces and a real image has formed infornt of the mirror.
Important Terms of Concave Mirror
[Image uploaded soon]
1)Pole
The center of spherical reflecting surface of the mirror has called the pole. It has denoted by P as shown in above given figure.
2)Centre of curvature
The centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part has called the centre of curvature. It has denoted by C as shown in above given figure.
3)Radius of curvature
The radius of the sphere of which the mirror is a part has called the radius of curvature. It has denoted by R as shown in above given figure.
4)Principal Axis
A line which has drawn through the pole of the mirror and the centre of curvature has called principal axis. It has shown in the above given figure.
5)Principal Focus
In the case of concave mirror, principle focus is the point at which all the parallel rays close to the principal axis converge after the reflection. It has also called the focal point. It has denoted by F as shown in above given figure.
6)Focal plane
A plane which is perpendicular to the principal axis and passes through the focal point has called focal plane. It is the plane where rays of light parallel with each-others but not parallel with the principal axis converge at it after reflection. It has shown in above given figure.
7)Focal length
The distance between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus has called focal length. Focal length of concave mirror is positive. It is denoted by small f as shown in above given figure.
8)Aperture
The diameter of the boundary of the mirror is called aperture. XY is the aperture in above given figure.
Image Formation in the case of Concave Mirror
Image is the visual represention of something. In the case of concave mirror, when two rays of light comming from an object meet at a point after reflection then an image is formed at that point. Image formed by the mirror is real if the the reflected rays of light converge at a point. Whereas image formed by the mirror is virtual if reflected rays of light appears to diverge from a point when produced backwards. Mostly, image formed by the concave mirror is real encept when the object is between focus(F) and pole(P) of the mirror. During the formation of image it is assumed that rays of light are paraxial means that they incident at points close to the pole(P) of the mirror and make small angle with the principle axis.
Different types and size of image can be obtain by changing the position of object from the concave mirror in the case of concave mirror. Therefore different types and size of image can be obtained in the case if concave mirror when object is placed:-
- At infinity
- Beyond the centre of curvature
- At the centre of curvature
- Between the centre of curvature and principal focus
- At the principle focus
- Between the principle focus and the pole of mirror
For detail study of image formed by concave mirror in these six cases with diagrams and characteristics visit Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Qsolution's post.
Method To Draw Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror
Ray diagram is a tool that has used to determine the size, location, orientation and types of image formed by the mirror. Before drawing the ray diagram of concave mirror you need to learn rules of reflection which has listed below:-
- When a ray of light is coming parallel to the principle axis, it converses at the focus after reflection.
- When a ray of light is coming through the focus, it passes parallel to the principle axis after reflection.
- In the case a ray of light is coming through the centre of curvature, it passes through same way after reflection.
- when a ray of light is incidence on pole of mirror, it reflects under the laws of reflection applied.
Now step by step method for drawing the ray diagram of concave mirror when the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature has listed below:-
Step.1:- Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays travelling towards the mirror as shown in given figure below.
[Image Uploaded Soon]
With the help of scale, draw one ray exactly passes through the focus of the concave mirror. Again draw second ray which travels exactly parallel to principal axis of the concave mirror. Then place arrow-heads on the rays to indicate its direction.
Step.2:- When these incident rays strike the reflecting surface of the concave mirror, then reflect them according to the rules of reflection as shown in the given figure below.
[Image Uploaded Soon]
The ray that passes through the focus of the concave mirror, travels parallel to the principle axis of the mirror. And the ray that travels parallel to the principal axis, passes throuth the focus of the mirror. Both the rays must be drawn using scale. Then place arrow-heads on it to indicate its diraction. After that extend the reflected rays passing their intersecting point.
Step.3:- Mark the image point of the top of the object as shown in the given figure below.
[Image Uploaded Soon]
The image point of the top of the object is the point where there two reflected rays intersect. If the third incident and reflected ray is drawn, then the third reflected ray also passes throuth this point of intersection. This is the point merely where all the light rays came from the top of the object intersect after the reflection. Rest of the image can be obtained by repeating these steps for another choosen intersecting point.
Step.4:- Repeat the process for the bottom of the image.
[Image Uploaded Soon]
After completing the first three steps, only the image of the top of the object has formed. Hence, the process must be repreated for the point on the bottom of the object. If the bottom of the object lies on the principle axis as in the given above figure, then the image of this point also lies on the principle axis at the same distance from the mirror as the image of the top of the object. The entire image can be filled at this point.
Same method works for drawing the ray diagram in the case of concave mirror for any position of the object.
Magnification in the case of Concave Mirror
Magnification is defined as the increase in the size if the image prosuced by the concave mirror with respect to the size of the object. It is also defined as the ratio of height of the image to the height of the object and denoted by 'm'. The magnification produced by the concave mirror can be expressed as




No comments: