Introduction
In the concave mirror ray diagram Qsolution's post, you are going to learn:-
- About concave mirror
- About concave mirror ray diagram
- Rules for constructing ray diagram
- summary in table
Concave mirror
Concave mirror is a spherical Curved mirror in which reflection takes place in the inner surface of the sphere of which the mirror is a part. Concave mirror has depressed inward at middle on the reflecting surface. Outer surface of the concave mirror has painted as shown in figure below:-
Concave mirror converges the rays of light when they strike on the reflecting surface of the mirror. Hence, it is also known as the converging mirror. When an object is very close to the concave mirror within focus, a magnified and virtual image has obtained. But if the distance between mirror and object increases, the size of image reduces and a real image has formed.
Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror
Ray diagram is a tool that has used to determine the size, location, orientation and types of image formed by the mirror. Before drawing the ray diagram of concave mirror you need to learn rules for constructing ray diagram which has listed below:-
- When a ray of light is coming parallel to the principle axis, it converses at the focus or appears to diversge through the focus after reflection.
- When a ray of light is coming through the focus or towards the focus, it passes parallel to the principle axis after reflection.
- In the case a ray of light is coming through the centre of curvature or towards the centre of curvature, it passes through same way after reflection.
- when a ray of light is incidence on pole of mirror, it reflects under the laws of reflection applied.
While drawing the ray diagram of concave mirror you will find six cases which are listed below:-
- When an object is at infinity.
- When an object is beyond the centre of curvature.
- In the case an object is at the centre of curvature.
- When an object is between the centre of curvature and principal focus.
- In the case an object is at the principal focus.
- When an object is between the principal focus and pole.
1)Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror when an object is at infinity
When an object has placed at inifinity infornt of mirror, a very very small real image has formed at the focus of the mirror. For example, suppose an object AB has placed far away from the mirror almost at infinity as shown in figure below:-
Since the incident rays of light from the object AB are coming parallel to the principle axis. Then they meet at focus after the reflection. Hence, a very small image is formed at the focus. Characteristics of Image formed by concave mirror when an object is at infinity has listed below:-
- Real image has formed.
- Inverted image has formed.
- Highly diminished image has formed.
- Image has formed at the focus infornt of the mirror.
2) Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror when an object is beyond the centre of curvature
When an object has placed beyond the centre of curvature of mirror. Then a small real image has formed between the focus and centre of curvature. For example suppose an object AB has placed beyond the centure of curvature C as shown in figure below:-
Since an incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming parallel to the principle axis. Then it passes through the focus F after the reflection. Another incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming through the centre of curvature C. Then it returns back along the same path. Both reflected rays of light meet at point B'.Hence, a small real image A'B' has formed at B' between the centre of curvature C and the pole P.
Charecteristics of image formed by the convex mirror when an object has placed beyond the centre of curvature has listed below:-
- Real image has formed.
- Inverted image has formed.
- Diminished image has formed.
- Image has formed between the centre of curvature and the pole.
3)Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror when an object is at the centre of curvature
when an object has placed at the centre of curvature of mirror. Then an inverted real image of same size has formed at the centre of curvature.For example suppose an object AB has placed at the centre of curvature C as shown in figure below:-
Since an incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming parallel to the principle axis. Then it passes through the focus F after the reflection. Another incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming through the focus F. Then it returns back parallel to the principle axis after reflection. Both reflected rays of light meet at point B'. Hence, an inverted real image A'B' of same size as object has formed at B'at the centre of curvature.
Charecteristics of image formed by the concave mirror when an object has placed at the centre of curvature has listed below:-
- Real image has formed.
- Inverted image has formed.
- Same size of image has formed.
- Image has formed at the centre of curvature.
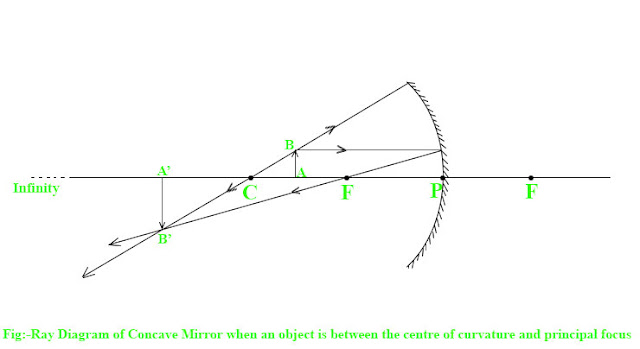
4)Ray Diagram of Concave Mirror when an object is between the centre of curvature and principal focus
when an object has placed between the centre of curvature and principal focus of mirror. Then a real magnified image has formed behind the centre of curvature. For example suppose an object AB has placed between the centre of curvature C and principal focus P as shown in figure below:-
Since an incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming parallel to the principle axis. Then it passes through the focus F after the reflection. Another incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming through the centre of curvature C. Then it returns back along the same path. Both reflected rays of light meet at point B'. Hence, a real magnified image A'B' has formed at B' behind the centre of curvature.
Charecteristics of image formed by the concave mirror when an object has placed between the centre of curvature and principal focus has listed below:-
- Real image has formed.
- Inverted image has formed.
- Magnified image has formed.
- Image has formed behind the centre of curvature.
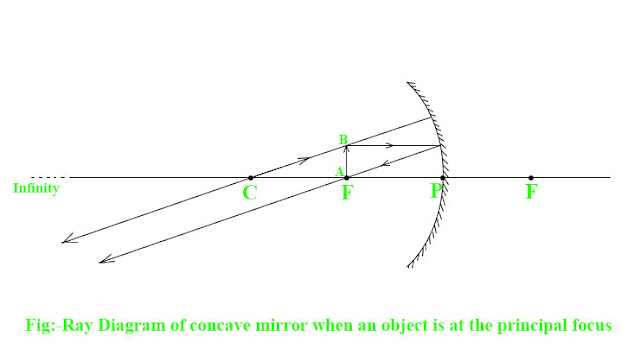
5)Ray Diagram of concave mirror when an object is at the principal focus
When an object has placed at the principal focus of the mirror. Then a very very large real image has formed at the infinity. For example suppose an object AB has placed at the principal focus P as shown in figure below:-
Since an incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming parallel to the principle axis. Then it passes through the focus F after the reflection. Another incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming through the centre of curvature C. Then it returns back along the same path. Both reflected rays of light are parallel to each others and meet eachother at infinity. Hence a very very large real image has formed at the infinity.
Charecteristics of image formed by the concave mirror when an object has placed at the principal focus of mirror has listed below:-
- Real image has formed.
- Inverted image has formed.
- Highly magnified image has formed.
- Image has formed at the infinity.
6)Ray diagram of concave mirror when an object is between the principal focus and the pole
when an object has placed between the principal focus and the pole of mirror. Then a large virtual image has formed behind the mirror. For example suppose an object AB has placed between the principal focus and the pole as shown in figure below:-
Since an incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming parallel to the principle axis. Then it passes through the focus F after the reflection. Another incidence ray of light from the object AB is coming through the centre of curvature C. Then it returns back along the same path. Both reflected rays of light are diverging, extend behind the mirror and meet at B'. Hence a large virtual errect image A'B' has formed at B' behind the mirror.
Charecteristics of image formed by the concave mirror when an object has placed between the principal focus and the pole of the mirror has listed below:-
- Virtual image has formed.
- Errect image has formed.
- Magnified image has formed.
- Image has formed behind the mirror.
Summary in Table
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Size | Image Nature |
| At infinity | At focus | Highly Diminished | Real and inverted |
| Beyond centre of curvature | Between focus and centre of curvature | Diminished | Real and inverted |
| At centre of curvature | At centre of curvature | Same size | Real and inverted |
| Between centre of curvature and focus | Beyond centure of curvature | Magnified | Real and inverted |
| At focus | At infinity | Highly Magnified | Real and inverted |
| Between the focus and pole | Behind the mirror | Magnified | Virtual and Errect |









good
ReplyDelete